How to amend a git commit
3 ways to undo a git commit
There are three commonly used approaches a developer can take to undo their last Git commit and put a new commit in its place:
- A git revert followed by a new commit.
- A git reset followed by a new commit.
- A simple git commit amend command.
Of those three, the option to amend a git commit is by far the easiest.
How to amend a git commit
To undo and remove the last commit in your history with the git amend command follow, these steps:
- Add, update or remove files as required to fix your local workspace.
- Stage your updated files with the git add –all command.
- Perform a git commit –amend command to undo the previous commit.
Git commit remove vs git amend
When you amend a Git commit, this removes the old commit from your branch’s history, and a brand new commit with the updated state of your workspace is put in its place.
The old commit becomes orphaned in your local workspace. The new, amended commit replaces the previous commit at the tip of the currently selected branch.
As such, it is more accurate to say the git commit amend command amends the Git commit history as opposed to amending the last commit itself. When you do an amend, you remove a Git commit from the branch history, rather than update or change the existing one.
| Git, GitHub & GitHub Copilot Certification Made Easy |
|---|
| Want to get certified on the most popular AI, ML & DevOps technologies of the day? These five resources will help you get GitHub certified in a hurry.
Get certified in the latest AI, ML and DevOps technologies. Advance your career today. |
Git commit amend example
Here is a simple git commit amend example that undoes the commit that added a file named alpha.txt to the repository.
The amended Git commit in this example not only removes the alpha.txt file from the commit history, but it also adds a new file named bravo.txt.
$ touch alpha.txt $ git add alpha.txt $ git commit -m "undo this git commit!" $ rm alpha.txt $ touch bravo.txt $ git add --all $ git commit --amend "undo the previous git commit"
There are three ways to undo a git commit:
✅git commit –amend
✅git reset –hard
✅git revertTo me, the amend approach is easiest, but like the reset command, it creates an orphan commit.
For shared commits, git revert is safest.https://t.co/pmI7Lzn4iP
— Cameron McKenzie | Docker | GitHub | AWS | Java (@cameronmcnz) November 28, 2023
Benefits of the git commit amend command
By far, the easiest way to undo a previous commit is with the git commit amend command.
Both the reset and revert approaches require the user to issue an extra command to undo the previous Git commit. With the git commit amend command, you simply edit files and perform a single commit as you normally would, with the only change being the addition of the –amend flag.
The git commit amend option is simple and easy to use.
Git commit amend vs git reset
A limitation of the git commit amend command is that it only applies to the most recent commit.
In contrast, the git reset command can undo any number of commits in your local history. A hard reset goes even further, restoring all files in your workspace to the exact state of a previous commit, something amend cannot do.
Both git commit amend and git reset have another issue: they generate orphan commits in your local repository.
For this reason, these commands should only be used to undo local commits that have not yet been pushed to a remote repository or pulled from a shared branch. Amending or resetting shared commits will disrupt the history for the entire team.
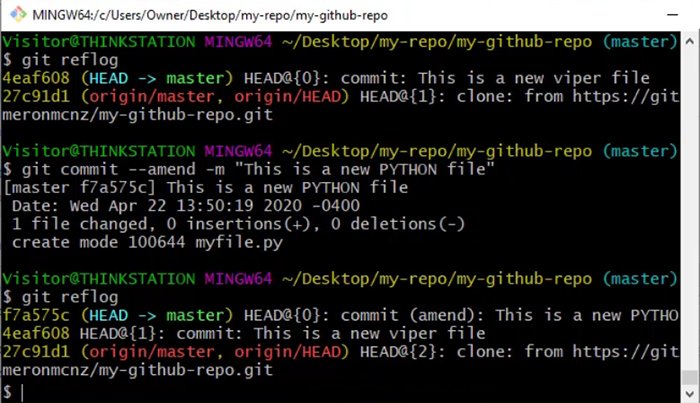
The git commit amend command is often used to quickly update or change a Git commit message.
Git commit amend vs git revert
When you undo a Git commit with reset instead of amend, the old commit remains in your history and a new commit is created to represent the undone change. For this reason, the git revert command is generally the safer option when working with a shared repository.
That safety comes with a drawback, though. Because a revert preserves the original commit, any mistakes you were trying to remove stay in your local history and are pushed to platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. In other words, the error becomes part of the permanent project history.
By contrast, when you undo a commit with amend, the old commit is discarded. It never appears in git log and is not shared externally; its existence can only be seen with git reflog.
There are many ways to back out of a commit, but if the change hasn’t been pushed or pulled to a shared repository, using git commit –amend is usually the simplest and cleanest solution.
Cameron McKenzie is an AWS Certified AI Practitioner, Machine Learning Engineer, Solutions Architect and author of many popular books in the software development and Cloud Computing space. His growing YouTube channel training devs in Java, Spring, AI and ML has well over 30,000 subscribers.




