Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
What is Remote Method Invocation (RMI)?
Remote Method Invocation (RMI) is an application programming interface (API) in the Java programming language and development environment. It allows objects on one computer or Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to interact with objects running on a different JVM in a distributed network. Another way to say this is that RMI provides a way to create distributed Java applications through simple method calls.
RMI is the Java version of what's known as a remote procedure call (RPC), but with the additional ability to pass one or more objects along with the request. It enables remote communication between applications using two objects -- stub and skeleton -- and is supplied as part of Sun Microsystems' Java Development Kit (JDK) in the package java.rmi.
An RMI request in Java is a request to "invoke" the method of a remote object. It has the same syntax as a request to invoke an object method in the same (local) computer. Objects can include information that will change the service performed in the remote computer. Sun Microsystems, the inventors of Java, calls this behavior "moving behavior" and the object parameter-passing mechanism "object serialization."
For example, when a user at a remote computer, A, fills out an expense account, the Java program interacting with the user could communicate, using RMI, with a Java program in another computer, B. Computer B always has the latest policy about expense reporting. In reply, the program in Computer B would send back an object and associated method information that would enable Computer A's program to screen the user's expense account data in a way consistent with the latest policy. If the policy changes, a change would be required to a program in only one computer (Computer B).
Need for Remote Method Invocation
Typically, distributed applications in Java need to locate a remote method. They also need to communicate with remote objects and load the class definitions for these objects. RMI is required to satisfy all these needs.
As an API, RMI enables client and server communications over the internet, allowing for client programs to send requests to a server program and the server program to respond appropriately to incoming requests from client programs. With RMI, a Java programmer can create a publicly accessible remote server object. This object facilitates seamless client-server communications through simple method calls on the server object. Client programs can communicate directly with the server object and with each other using a URL and HTTP.
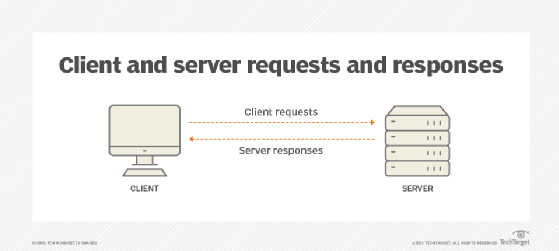
In Java, RMI is designed to preserve the object model and its advantages across a network. It also minimizes application complexity, preserves type safety, and makes it easy to work with both local and remote objects.
Three-layer implementation model
In Java, RMI is implemented as three layers:
1. Stub program. The stub program is on the client side of the client-server relationship. There is also a corresponding skeleton at the server end. To the calling program, the stub appears as the program being called for the service. Sun uses the term proxy as a synonym for stub.
2. Remote Reference Layer (RRL). The RRL layer can behave differently depending on what parameters the calling program passes. For example, it can determine whether the request is to call a single remote service or multiple remote programs (as in a multicast).
3. Transport Connection Layer. This third layer sets up and manages the request that travels down through the layers on one computer and up through the layers at the other end. Essentially, it establishes a network connection between the client's stub and RRL, and the server's skeleton and RRL.
Remote Method Invocation stub and skeleton
Stub and skeleton are both RMI objects that enable communications with remote objects in Java programs. A remote object simply means an object whose method can be invoked remotely from another JVM.
The stub functions as a gateway for the client side by routing the client's outgoing requests. When the caller invokes a method on the stub object, the stub first initiates a connection with the JVM. It then writes and transmits the parameters to the JVM, reads the return value (or exception) and returns this value to the caller.
The skeleton also acts as a gateway, albeit for the server side. Like the stub, it receives and routes all incoming requests by reading the parameter for the remote method, invoking the method on the actual remote object and transmitting the result to the caller.
Both a server program and client program are required in an RMI application. The server program resides on the server. A remote object is created inside this program. The client program resides on the client and a reference of the server's remote object is made available for the client. The client program can request the server's remote objects and invoke its methods. With the RRL in place, a virtual connection is established between the client and server and references made by the client to the remote object are managed.
How a Remote Method Invocation application works
Suppose a word processing program is installed on a server for enterprise use. An authorized user, or client, on the network who wants to use the program double clicks on the icon on their desktop graphical user interface (GUI). They may also access the program by typing the program name in a command line or search box.
The client's invocation to the remote object on the server sends a request to the server. The stub receives this request and passes it on to the client-side RRL. On receiving this request, the RRL invokes a method and passes the request to the server-side RRL. This RRL then passes the request to the server's skeleton, which invokes the required object on the server and then passes on the result to the requesting client. At this point, the user can access and use the software.
Marshaling and unmarshaling in Remote Method Invocation
When the client-side stub writes and transmits the parameters to the remote VM, the process is known as marshaling. Marshaling happens when the client invokes a method that accepts parameters on a remote object. Typically, these parameters, which may be of primitive type or objects, are bundled into a message before being sent over the network. Primitive type parameters are put together with an attached header, while object parameters are serialized. Marshaling also happens when the server-side skeleton writes and transmits the result of an incoming request to the client (after reading the parameter for the remote method and invoking the method on the remote object).
Unmarshaling happens when the stub object reads the return value or exception from the remote JVM. After unmarshaling, it returns the value to the caller, or client. This also happens at the server side when the packed parameters are unbundled, and the required method is invoked.
Remote Method Invocation Registry
RMI Registry is a server-side naming repository or namespace that contains all remote server objects, each with a unique bind name. It allows remote clients to get a reference to these objects. Whenever a server creates an object, the object gets registered with the registry using either the bind() or reBind() method. The client invokes a remote object and fetches it from the registry by using its bind name and lookup().
Before using the RMI registry, programmers must ensure that the shell or window in which the rmiregistry command runs does not have a CLASSPATH environment variable pointing to the remote object classes anywhere on the system. If the registry finds these classes when it starts, it will not load them from the server-side Java VM, which will then prevent clients from downloading the remote server classes and from accessing the remote program.
Also, the RMI registry usually starts on the default 1099 port. However, programmers can specify a different port. In this case, it's important to specify the same port number in the server-side code as well.
Learn seven benefits of Java and explore the top Java programming tools used in application development.










